By Jayatheswary A/P Parnealsivam, Lecturer, School of Allied Health Sciences
Introduction
A medical laboratory technologist (MLT) is a profession listed under the Allied Health Science (AHS) group. This profession is not well known among the general public because many of the tasks performed are done behind the scenes. Medical laboratory technologists are the backbone of the medical laboratory services because they are involved in all levels of laboratory work, from the pre-clinical to the clinical, and from the clinical to the post-clinical stages. They are involved in the process of diagnosing for treatment, rehabilitation and prevention through clinical laboratory tests.
Roles of MLTs in the Laboratory
The main function of an MLT is to conduct diagnostic tests in the laboratory in order to produce test results that will help doctors in making their very important diagnoses. This diagnostic test is conducted on a wide variety of specimens such as blood, urine, body fluids, faeces (stool) and tissue samples. Medical laboratory technologists are responsible for ensuring the suitability of the specimens that are obtained from patients. Accurate results must be given at the fastest possible time to the medical officer in ensuring effective treatment.
The following are the major fields in medical laboratory sciences:
- parasitology
- microbiology
- histopathology
- cytology
- hematology
- biochemistry
- blood-banking/immunohematology
There are many laboratory tests which are offered according to the needs and capacity of the respective health institutions. Each of these tests requires a distinctive individual sample and every sample must be sent to the laboratory in a container labelled as a biohazard. This is because all samples are considered as biohazards, things that may pose a risk to human health and the environment due to the biological processes. For example, the sample may be contaminated with HIV or the hepatitis virus and other infectious microorganisms.
Before commencing any laboratory work, medical laboratory technologists will equip themselves with suitable personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, masks, lab coats, and shoes. This PPE are worn in accordance with the work to be done. Medical laboratory technologists run all diagnostic tests including tests on tissues or body fluids such as urine, faeces, sputum or blood so that any abnormality in a patient’s current health status can be detected.
Some laboratory tests are carried out with the aid of automated machines. Therefore, medical laboratory technologists working in such laboratories should carry out quality control (QC) tests on the machines which are used to calibrate the results. QC ensures that the machines produce reliable and accurate test results.
The types of tests that require blood samples are:
- liver function tests
- renal function tests
- bilirubin (jaundice) tests
- cardiac function tests
- hormone tests
- blood cell count tests

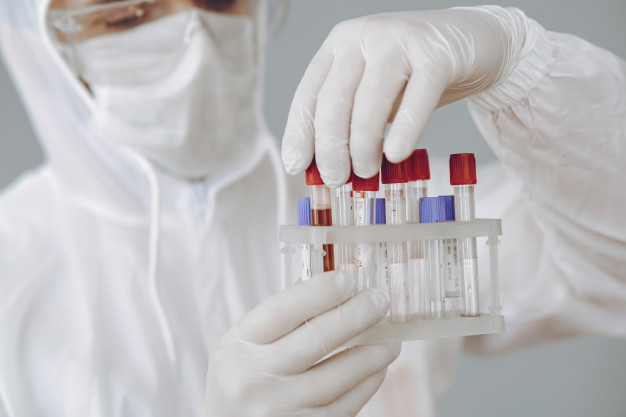
Figure 1: An MLT performing blood grouping test
The test that requires a sputum sample is the tuberculosis test. Some samples should be processed in a fume hood because the sample may release viruses or bacteria. In conducting the test, the medical laboratory technologist needs to get accurate test results as soon as possible so that the doctors can detect and treat the relevant health problems.
For patients who require a blood transfusion, the medical laboratory technologist will be solely responsible for testing the compatibility of blood between the blood donor and the patient’s blood. There is no room for error while running the compatibility blood test because the patient’s life is at stake. Blood donor screening must go through various stages before it is deemed safe for use.
In addition, medical laboratory technologists can also conduct some major procedures such as:
- bone marrow aspiration tests (BMAT)
- fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC)
- bedside blood grouping test directly from the patient
Usually, the BMAT test is performed for patients who are suspected of suffering from blood cancer (leukaemia) or to see the effectiveness of chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant. The FNAC test is carried out early to investigate lymphoma (a tumour that exists on the lymph node). The bedside blood grouping test is carried out to determine the grouping or patient’s blood type in order to see if there is any clash between the two blood group results. These reagents should be prepared by the senior medical laboratory technologist. This preparation requires experience, precision and accuracy. Usually, these tasks are done by the senior medical laboratory technologist as any damage to the reagent can invalidate the laboratory test results.
There are some initial laboratory screening tests that require blood film examination, for example, the blood cell count and peripheral blood film test. These tests require an MLT to insert a glass blood film slide under a microscope to detect or count the presence of blood cells that would be indicative of a particular kind of disease. Primary examples of diseases that require these tests are leukaemia, thalassemia, anaemia, malaria and dengue.
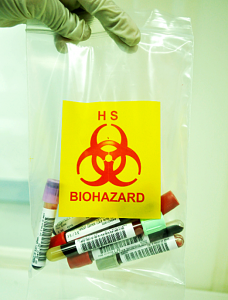
Figure 2 (a), (b): Methods of sample transfer to the laboratory
A medical laboratory technologist does not only test the samples provided but also has to ensure the proper procurement and transportation of samples. Blood samples that are sent in tube containers need to be ascertained that they are not lysed. Also, some of the tests cannot be carried out on clotted blood samples (clumping of red blood cells). Prior to the analysis, some samples should be put in appropriate containers (by sample type and test) and transferred in ice or other suitable chemical substances to the laboratory in order to ensure accurate test results. The results obtained must be accessible as soon as possible to the medical officers so that they can make a diagnosis and provide the necessary treatment. All body fluids and tissues can be tested to gather specific information. This is not only useful in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, but it is also important in the world of forensics in solving crimes.
The senior medical laboratory technologist must ensure that all the apparatus and machinery used are inspected and maintained regularly so that they are always in good condition. These machines are tools that can help the medical laboratory technologist in conducting the laboratory tests. The senior medical laboratory technologist is also responsible for reporting the number of tests carried out and the workload to upper management. This is to facilitate manpower-planning needs and expenses in the future. In the management of the laboratory, the Senior Medical Laboratory Technologist is responsible for ensuring that the supplies of consumables and disposables are always sufficient.
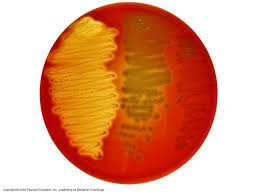
Figure 3: Blood agar with Alpha, Beta and Gamma Hemolytic patterns
Medical laboratory technologists who are involved in medical research help to carry out tests in the study of diseases or the effects of recent medication. There is also The Animal House or laboratory animal resource unit where animals such as mice, monkeys, rabbits, guinea pigs and hamsters are kept and bred for research purposes. Laboratory animals will be supplied to researchers at universities and other government research agencies. The research that is done helps to enhance test methods in making them more accurate and effective. It also contributes to the development of technology that is used in laboratories.
In order to upgrade the medical laboratory services, medical laboratory technologists need to have more expertise and skills by furthering their education from a diploma to a bachelor, master or doctorate level. Many institutions of higher learning are now offering educational programmes appropriate for medical laboratory technologists who are interested in pursuing higher education.
Conclusion
All medical laboratory technologists have certain common characteristics. They are problem solvers. They love challenges and take responsibility and accountability for all their tasks. They produce work that is accurate and reliable, even under pressure. They communicate well in written and oral form. They set high standards for themselves and emphasise quality in the work that they do. They are very committed to their careers and are interested in all areas of medical laboratory science. For those who choose a career in the field of medical laboratory science, the exploration never ends.